Describe a Testcross and Identify When It Is Useful
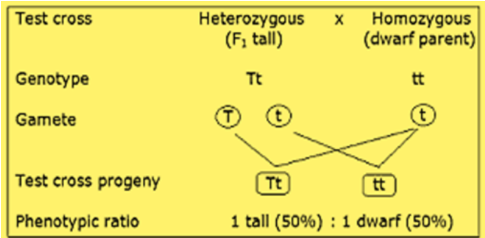
We do not know whether given plant is homozygous tall TT or heterozygous tall Tt. The purpose of the test cross is to determine the genetic makeup of the dominant organism.
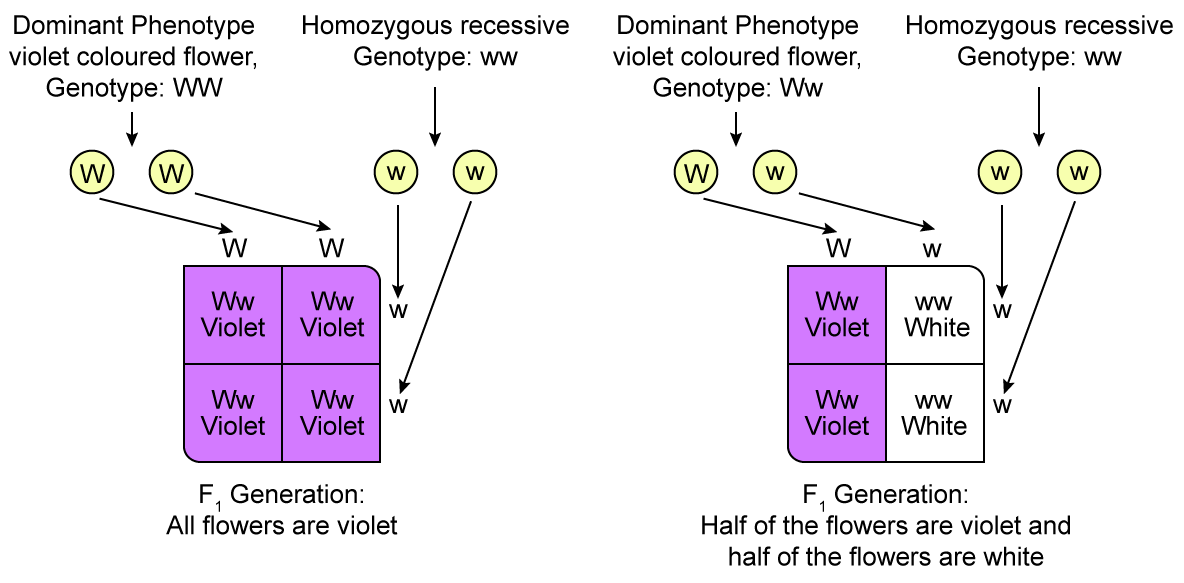
Define And Design A Test Cross Biology Topperlearning Com Jjpfb
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS.

. December 4 2014 Posted by DrSamanthi. In pea plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness. Identify the parental classes ABC and abc with no crossover.
A test cross is a cross between an individual with an unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive genotype. O Identify the parental types and the recombinant types in the testcross progeny. Mar 26 2018 Test cross is done to determine the genotype of a plant regarding a particular trait.
Write out all the possible gamete genotypes that can be produced from the tester. If the progenies produced by a test cross show 50 dominant trait and 50 recessive trait then the unknown individual is heterozygous for a trait. Identify the order and distance between the genes.
Describe ONE fitness cost to the female of mating with this particular male. It tests whether the trait is pure or not by mating the dominant trait with a recessive trait. When we cross our fly of interest to a tester we can directly read the genotype of each gamete from.
If any of the F1 hybrids have a recessive pheotype then we know that the dominant parent was heterozygous. The classic Mendelian dihybrid cross ratio round yellow. The key difference between test cross and backcross is that the test cross is the cross that occurs between a dominant phenotype and a recessive phenotype while the backcross is the cross that occurs between generation F1 hybrid and one of the two parents.
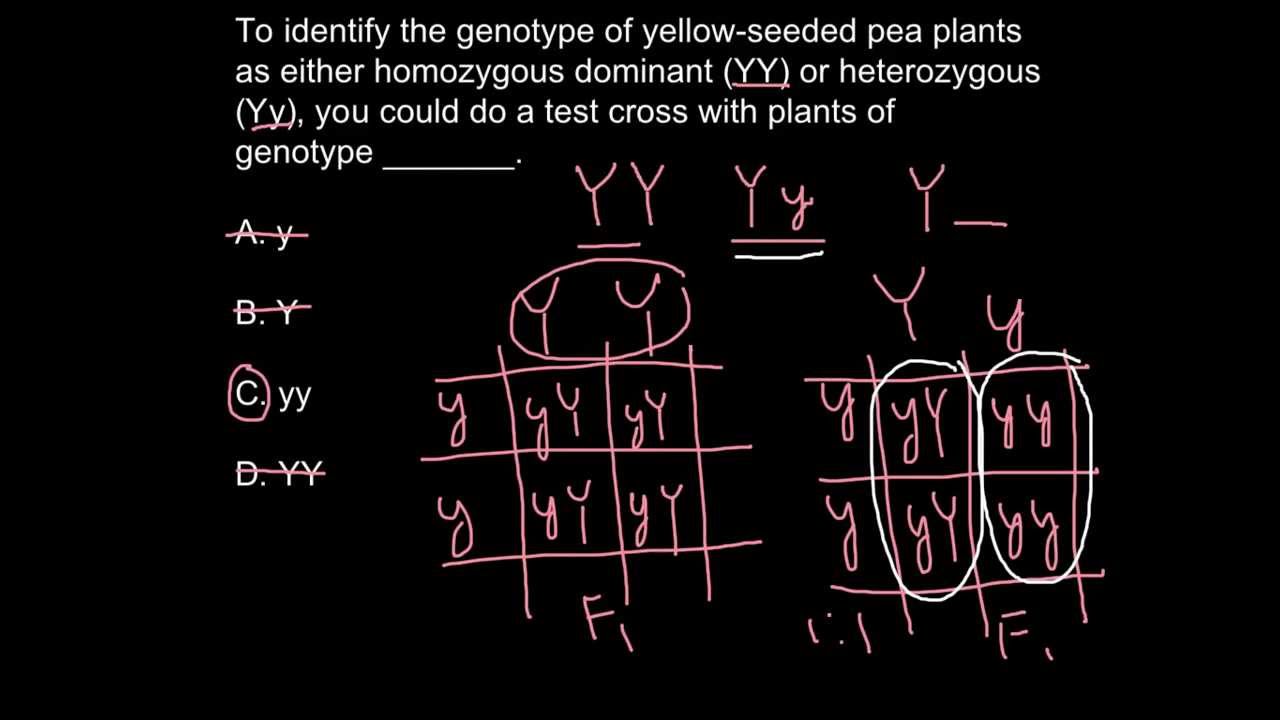
The pattern of observed phenotypes in the offspring can determine the unknown genotype of the parent. Early use of the test cross was as an experimental mating test used to determine what. 1 point Identify difference 1 point The majoritygreater than 50 percent would have the parental plant phenotypes.
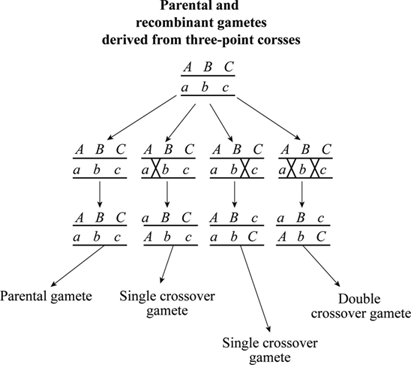
Define sex linkage and identify two examples of sex-linked conditions Outline why X-linked recessive disorders are more common in males Describe the inheritance and cause of the following genetic diseases. Because a double crossover switches the gene in the middle with respect to the genetic markers on either side of it it is used for determining the gene order. C If the two genes were genetically linked describe how the proportions of phenotypes of the resulting offspring would most likely differ from those of the testcross between an F 1 individual and a ggdd individual.
1 Answer Krishan T. It is used to determine whether the individual is homozygous or heterozygous for a trait. Analyzing data from crosses to determine map distances for two genes at a time makes the process time consuming and tedious.
Lets take a tall pea plant of unknown genotype. Use pink labels to identify the progeny genotypes and white labels to identify the progeny frequencies. At least one Z or Z chromosome is necessary for survival of the fish.
O Create a table presenting the results of the cross listing each trihybrid gamete genotype and the number of progeny showing that phenotype. Click here to view We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization. Up to 24 cash back A test cross is a way to determine the genotype of an organism.
Gene mappers are motivated to map all of the tens of thousands of genes found on the chromosomes of plant or animals. Good general combining ability is needed in the first testcross and subsequent testing identifies the exact combinations with commercial potential. Again intuitively double crossover occur much less frequently than a single crossover.
The genetic makeup of an individual is known as its genotype. O Analyze the loci two at a time determining the recombinant frequency. The organism in question is coerced with an organism that is homozygous for the recessive trait and.
A systematic approach after the crossover can help 1. Therefore geneticists will often attempt to map as many genes as. A test cross is crossing an organism with unknown genotype to a recessive homozygote for a specific phenotype in order to determine dominance.
However the phenotype alone doesnt not tell you the genotype of an organism. A test cross is a cross of an individual of an unknown genotype dominate with an individual of a known genotype homozygous recessive. -To identify whether an organism exhibiting a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific allele a scientist can perform a test cross.
It is a method to determine the genotype of an organism. The genotype exhibits the alleles or the gene pattern carried by an organism. A testcross discovered by Mendel generally involves crossing of phenotypically dominant individual with a phenotypically recessive individual to determine the recombinant frequency and zygosity of the inherited genes.
Three Point Test Cross. Test cross the cross of an organism with an unknown dominant genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for that trait What does it do. An allele is never intrinsically dominant or recessive Instead these terms describe a relationship.
Testcross evaluation is used to assess combining ability. Based on the information identify the genotype of the male parent in the cross. A cross between AABBCC with aabbcc is done to obtain F1 progeny that is testcrossed with aabbcc homozygous recessive.
Map any two loci. If a known parent is homozygous recessive. A two-point testcross is done to determine the recombinant frequency between 2 linked genes.
Mendel wanted to do this so that he could be sure he was working with a dominant organism which was homozygous or contained only dominant alleles. A test cross can determine whether the individual being tested is homozygous dominant pure bred or heterozygous dominant hybrid. Test cross is a cross between an organism with unknown genotype and a recessive parent.
Testcrosses are used to determine whether an individual with dominant traits carry the recessive allele. Predicting hybrid performance by evaluating inbred lines themselves is not typically an efficient use of resources. Multiple Point Gene Mapping.
Identifies how a testcross is used to determine genotype. The purpose of using a tester is to ensure that the alleles provided by the non-tester parent fully determine the phenotype or appearance of the offspring. A test cross is a way to explore the genotpye of an organism.
A testcross is used to determine whether an individual expressing the dominant phenotype is homozygous dominant or heterozygous. We have a new and improved read on this topic. Understanding the difference between test cross.
A researcher crossed two fish and observed a 21 ratio of males to females among the offspring.

What Is A Test Cross Explanation With Examples Youtube

Mastering Biology Chp 14 Hw Flashcards Quizlet
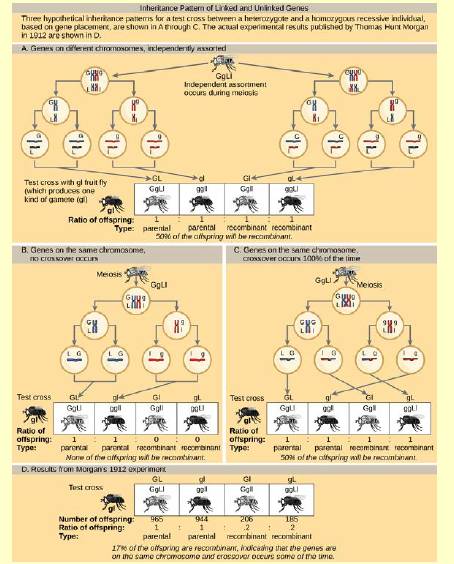
Figure 13 3 In A Test Cross For Two Characteristics Such As The One Shown Here Can The Predicted Frequency Of Recombinant Offspring Be 60 Percent Why Or Why Not Bartleby
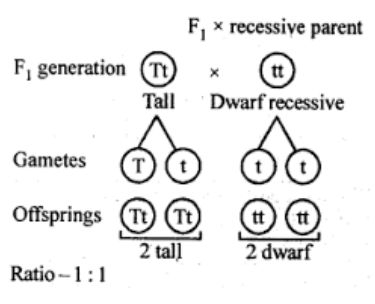
Define And Design A Test Cross Class 12 Biology Cbse
How Does A Test Cross Help In Identifying The Genotype Of The Organism Explain Biology Topperlearning Com Pqsgyoyy

Explain Test Cross With Suitable Example And State Its Ratios Biology Shaalaa Com
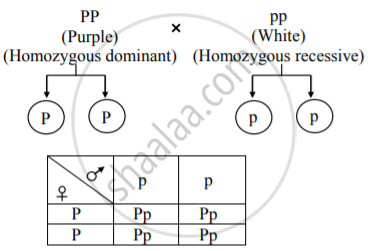
Explain Test Cross With Suitable Example And State Its Ratios Biology Shaalaa Com

What Does It Mean To Say That You Will Be Doing Crosses In Biology Lisbdnet Com
Definition Of Three Point Testcross Chegg Com
What Is A Test Cross Give Examples Class 12 Biology Cbse
What Is A Test Cross What We Use It For Youtube

A Test Cross Is Carried Out To Biology Questions

Test Cross Involves Biology Questions

Test Cross Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary

Define And Design A Test Cross Biology Shaalaa Com

How Does A Test Cross Help In Identifying The Genotype Of The Organism Explain


Comments
Post a Comment