Describe the Structure of Graphite With Properties and Uses
The structure of graphite consists of many flat layers of hexagons. The rings have many layers of particles.

Diamond 2 3 1 Aqa Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes 2018 Save My Exams
You can think of graphite rather.
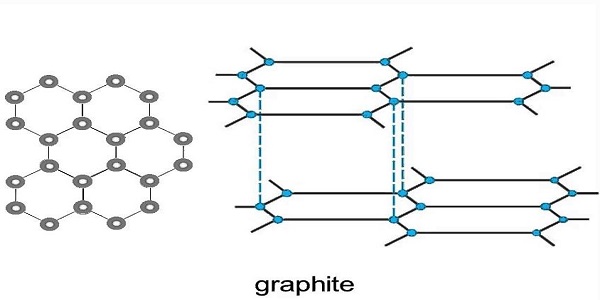
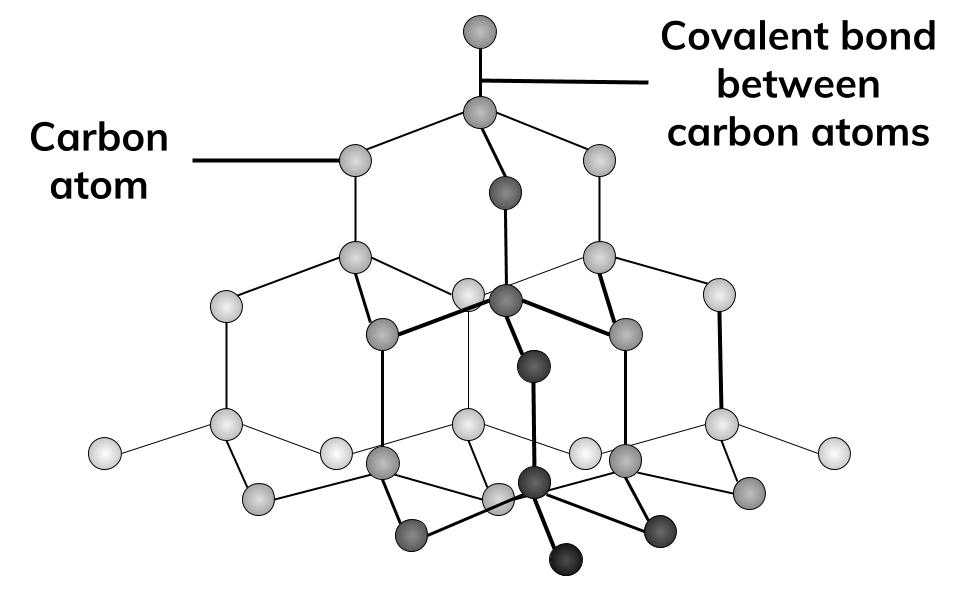
. Graphite is a big covalent structure with each carbon atom joined with three other carbon atoms with covalent bonds. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The various layers of carbon atoms in graphite are held together by weak Van.
Carbon is the 4th most common element in the Universe after hydrogen helium and oxygen. STRUCTURE Thermodynamically graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Brushes in electric motors.
It is also a very good conductor or electricity. The ideal graphite structure is shown in Figure 1-5. It finds its applications as a lubricant or an inhibitor in nuclear reactors.
Graphite is used for its thermal insulation lower rate of heat transfer properties. Diamond is transformed to graphite above 1500C 2732F Figure 1-4. The weak form of forces hold the sheet quickly.
Thermodynamically graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The layers can slide over each other easily. Graphite ˈɡræfaɪt is a crystalline form of the element carbon.
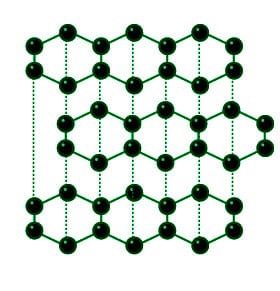
Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which. These carbon atoms form a layer like structure with a hexagonal arrangement of carbon atoms. This structure consists of planar layers of carbon atoms forming a hexagonal mesh pattern.
As an electrode material Conductor of electricity Graphite has delocalised electrons that can conduct electricity. Layer structure of graphite. All the carbon atoms in Graphite are said to have stable chemical bonds with that of the other three carbon atoms thus making the sheets that look like chicken wire.
4 PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF GRAPHITE ENTEGRIS INC. B The structure of graphite is very different from that of a diamond. When you use a pencil sheets are rubbed off and stick to the paperhas a high melting point similar to that of diamond.
Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. Graphite is an allotrope of the chemical element carbon and is denoted by the symbol C.
Graphite exists as one of the giant covalent structures in nature. Graphite has a high melting point similar to that of diamond. Diamond is trans-formed to graphite above 1500C Figure 1-4.
Graphite the other form of elemental carbon in addition to diamond adopts a very different covalent structure than that of the diamond to which different physical properties correspond. Each carbon atom in a graphite layer is joined to other three carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds to form flat hexagonal rings. Between layers are weak intermolecular forces which allows sliding of the layers on top of each other and so.
A graphite crystal consists of these layers of carbon atoms stacked. Graphite is a versatile industrial mineral with unique properties that have facilitated technological innovation beginning in the 16th century with discovery of high-grade lump graphite at. Wear your headset and share with your friend.
These layers facilitate electrical conduction. Weak forces of attraction exist between the layers. Used in pencils 3.
These layer slide over each other with ease. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms the carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. It consists of weakly bound layers of graphene stacked into a hexagonal structure.
The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon. The carbon atoms in graphite are bonded in flat hexagonal lattices and layered in sheets. In order to melt graphite it isnt enough to loosen one sheet from another.
For a non-metal graphite is a relatively good conductor of heat and electricity which gives it some similarity with metals. It has a soft slippery feel and is used in pencils and as a dry lubricant for things like locks. It finds many uses in daily life due to its properties.
This CrystalBenefits lists the physical and chemical properties of this element. USES OF GRAPHITE RELATION TO STRUCTURE 1. It is made up of carbon.
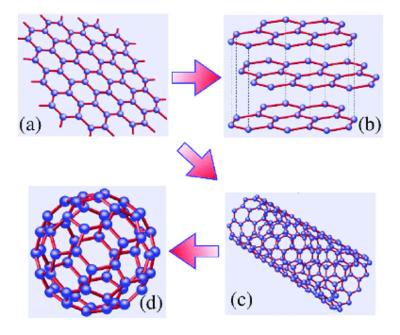
Graphite is made from layers of carbon which contain many 6-membered carbon rings hexagonal. Cylindrical fullerenes are referred to as nanotubes. The carbon atoms form layers of.
The electric charge OR thermal kinetic energy is quickly conveyed by the delocalised electrons. Graphite is arranged in layers. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which.
A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms. Compare this with the structure of diamond. Structure of Graphite and Uses Structure.
The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Buckyballs and buckytubes are terms used to describe them depending on their shape. Diamond and graphite both have giant molecular structure however in diamond carbon atoms link together to form giant lattice whereas in graphite the carbon atoms are arranged in layers and each carbon atom is only covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms and they are arranged in hexagons six-sided rings.
Each layer is held together by each carbon being covalently bonded to 3 other carbon atoms and this leaves a delocalised electron to move freely through the structure. You have to break the covalent bonding throughout the whole structure. Fullerenes have a similar structure to graphite which is made up of a sheet of connected hexagonal rings but they have pentagonal or sometimes heptagonal rings that prevent the sheet from being planar.
Each carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. Graphite is used in electrical contacts eg. Solid lubricant Smooth and slippery texture Graphite has a layered structure.

Pdf Graphite Properties Uses And South Australian Resources

Graphene Could Relieve World Water Shortage Sea Water Desalination An Annotated Infographic Nanotechnology Material Science Physics And Mathematics

Graphite An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Explain The Difference In Properties Of Diamond And Graphite On The Basis Of Their Structures
Diamond And Graphite Structure Uses Properties Applications Geeksforgeeks

Safe And High Quality Gasket Materials Are The Right Choice Material Inert Gas Safe
Graphene Structure And Shape Graphene Info

Graphite 2 3 2 Aqa Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes 2018 Save My Exams

Giant Covalent Structures Structure And Bonding Chemistry Year 10 Gcses Diagram Quizlet
1 50 Explain How The Structures Of Diamond Graphite And C60 Fullerene Influence Their Physical Properties Including Electrical Conductivity And Hardness Tutormyself Chemistry

What Is The Structure Of Graphite Engineering Choice

Difference Between Diamond And Graphite Comparison Summary Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Commonly Confused Words
Igcse Chemistry 2017 1 50 Explain How The Structures Of Diamond Graphite And C60 Fullerene Influence Their Physical Properties Including Electrical Conductivity And Hardness

What Is Graphite Definition Structure Properties Process Uses

Structure And Applications Of Graphite Semesters In

Open Knowledge Wiki What Is Graphite
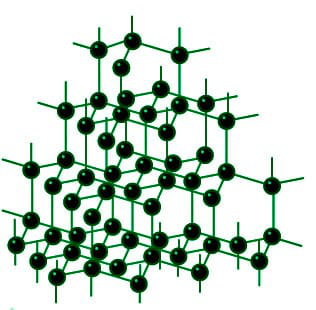
Diamond And Graphite Structure Uses Properties Applications Geeksforgeeks

Gcse Chemistry Electrolysis Of Lead Bromide Gcse Chemistry Gcse Science Revision Gcse Science
Comments
Post a Comment